| school_grade | Frequency_of_Students |
|---|---|
| 1 | 23 |
| 2 | 20 |
| 3 | 15 |
| 4 | 12 |
| 5 | 10 |
| 6 | 8 |
2.5.Displaying & Describing Data
Plots and Tables
2025-09-29
Outline
- Letting data type guide visualizations
- Rules of data visualization - principles of good plots
Cumulative Frequency Distributions
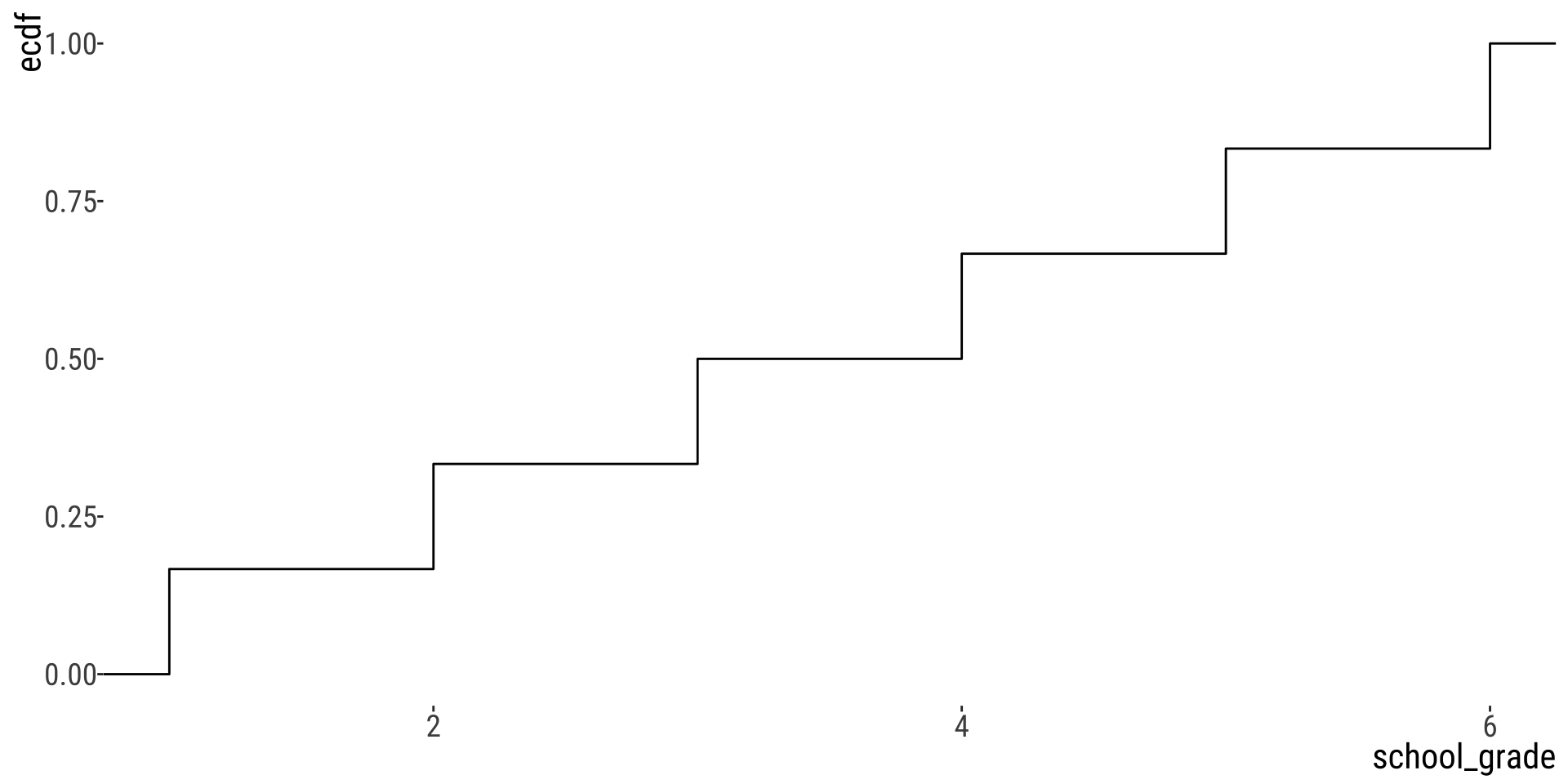
Number of students per grade
The cumulative frequency of a value is the proportion of individuals equal to or less than that value. In this case, equal or less than a given grade.
Sort data, calculate cumulative frequency…
Cumulative Frequency Distributions
- Sort all values
- Calculate the fraction of values \(\leq\) each value – the cumulative relative frequency
Code
school_grade Frequency_of_Students Cumul_Freq Rel_CFreq
1 1 23 23 0.2613636
2 2 20 43 0.4886364
3 3 15 58 0.6590909
4 4 12 70 0.7954545
5 5 10 80 0.9090909
6 6 8 88 1.0000000Cumulative Frequency Distributions
- Plot the values on the \(x\) and their cumulative relative frequencies on the \(y\)
- Connect the values with lines
Cumulative Frequency Distributions
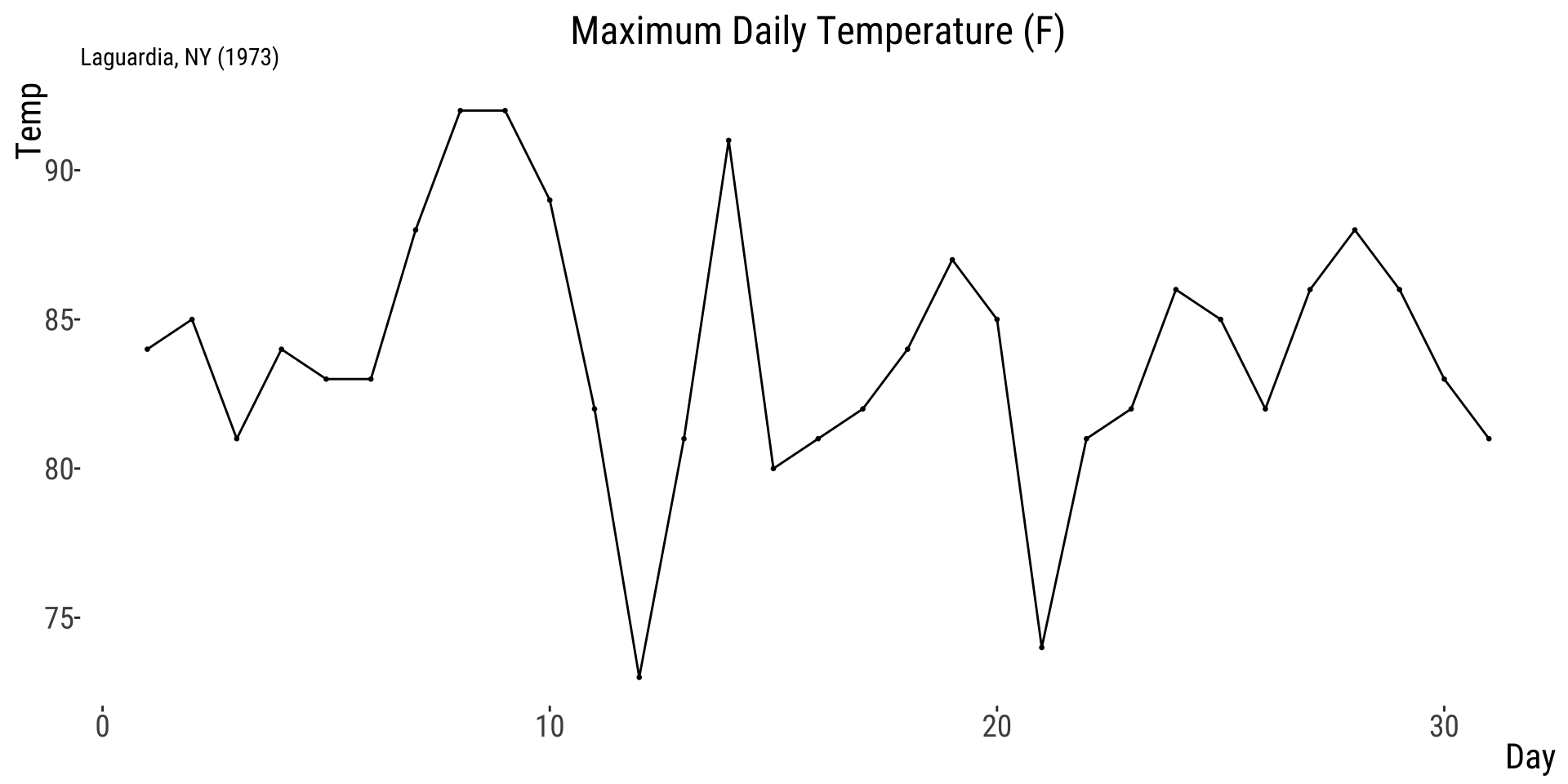
example 2: Temperatures near LaGuardia (1973)
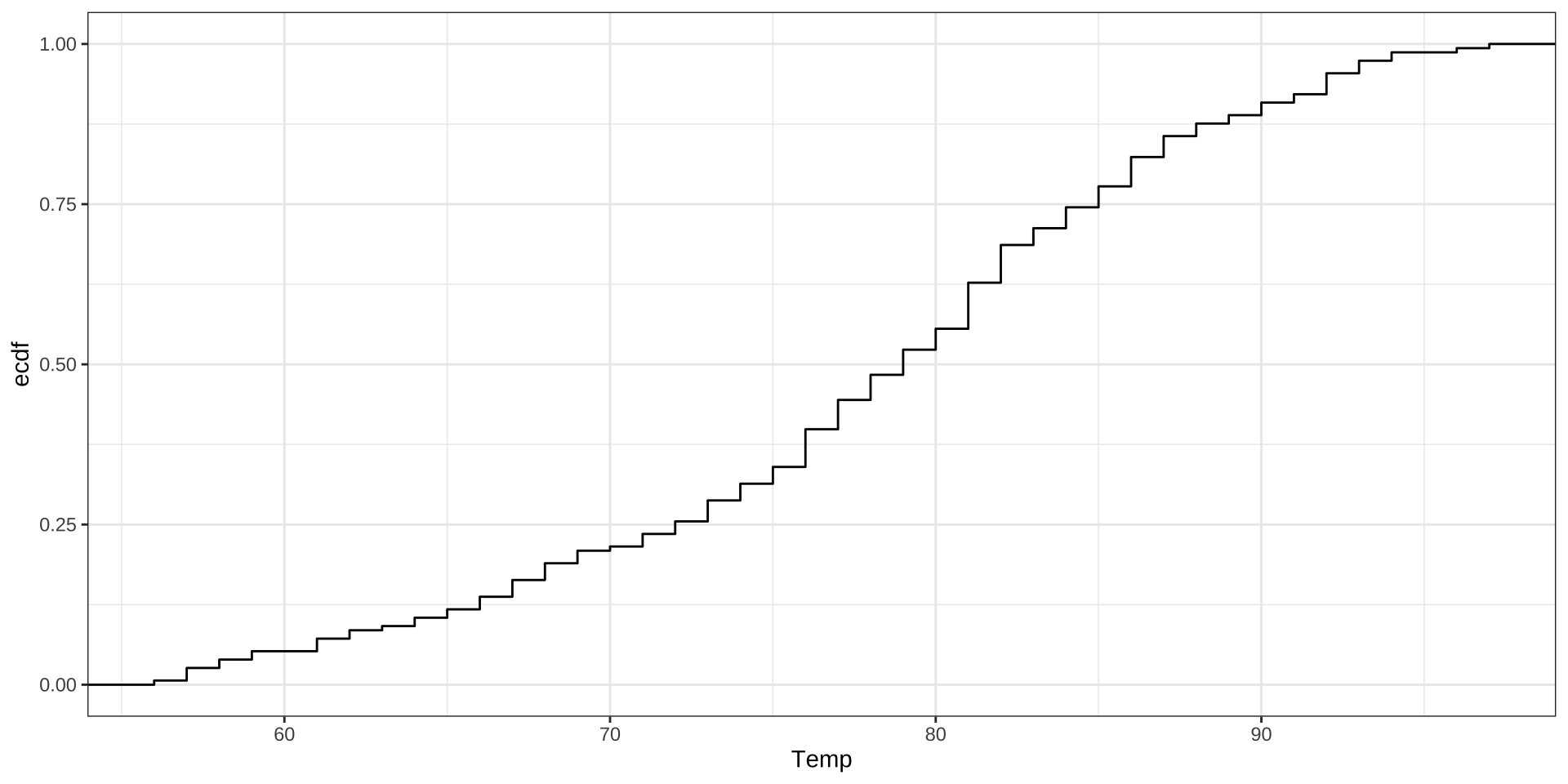
ECDF: empirical cumulative distribution function
Cumulative Frequency Distributions
Example 3: Spider running speed
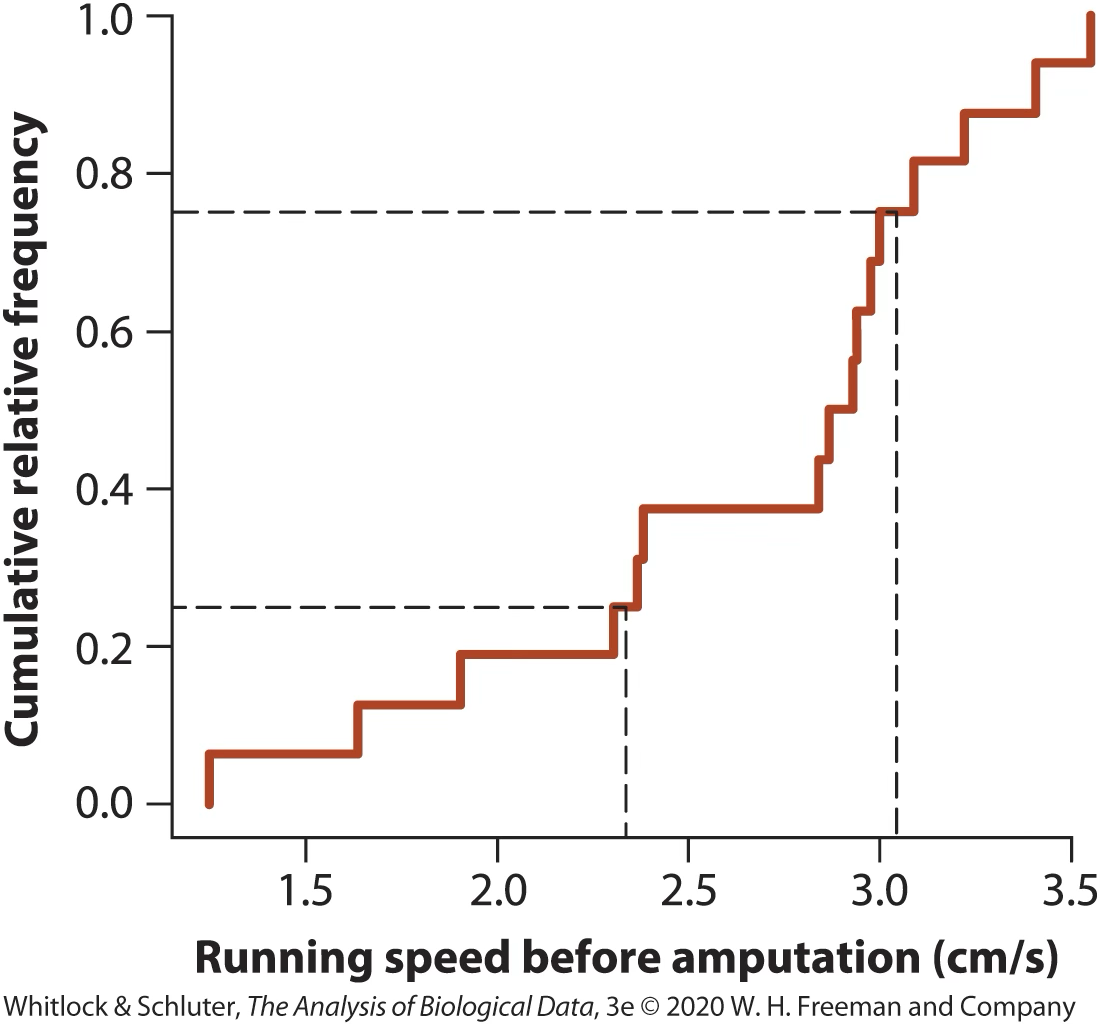
Figure caption: Figure 3.4-1 from the textbook
Cumulative frequency distributions clearly communicate quantiles.
Histograms, density plots, & cumulative frequency plots …
can reveal the shapes of distributions
important for understanding data
and choosing a statistical approach
Distribution shapes
Histograms
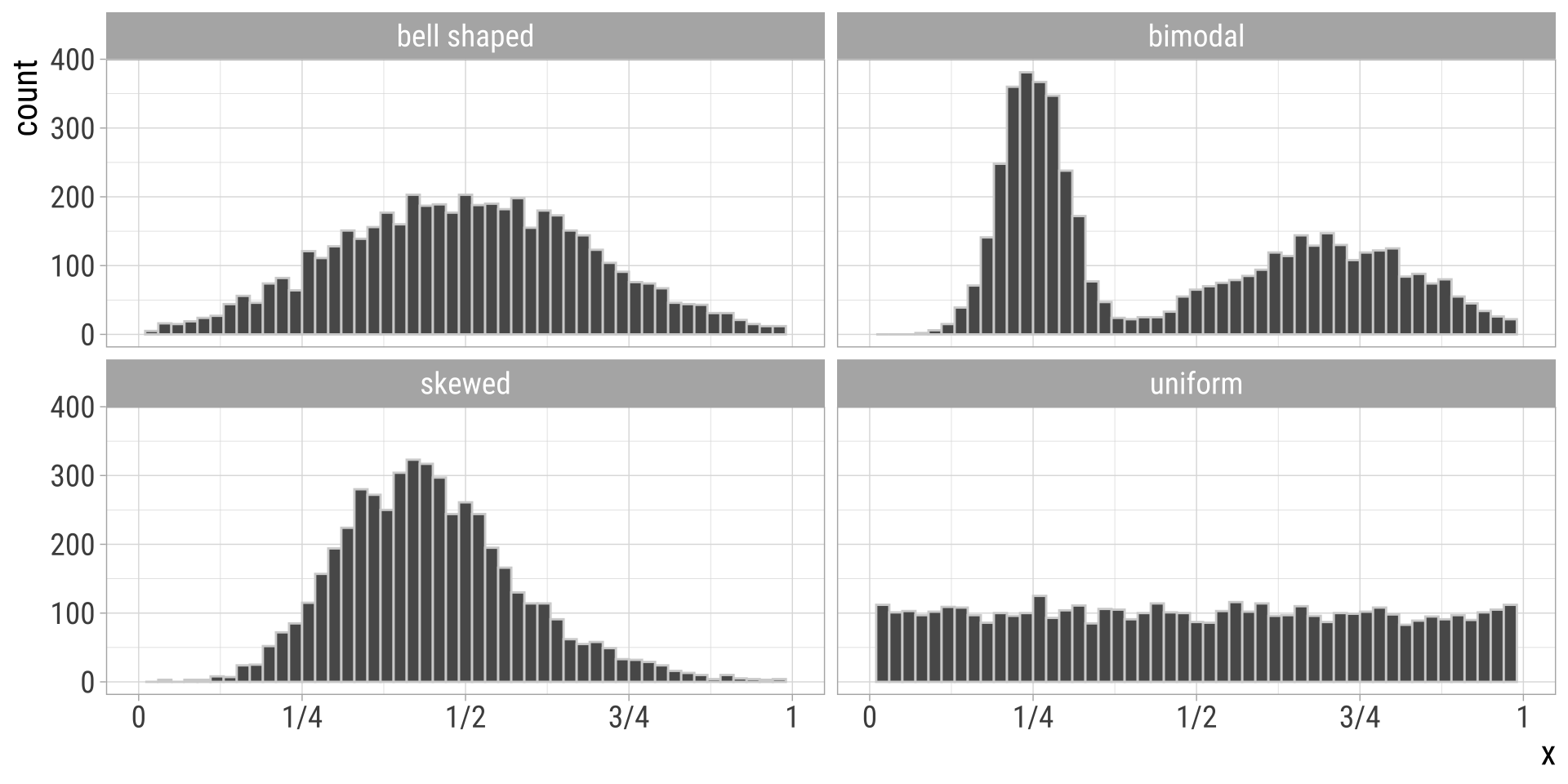
Distribution shapes
Cumulative Frequency Distributions
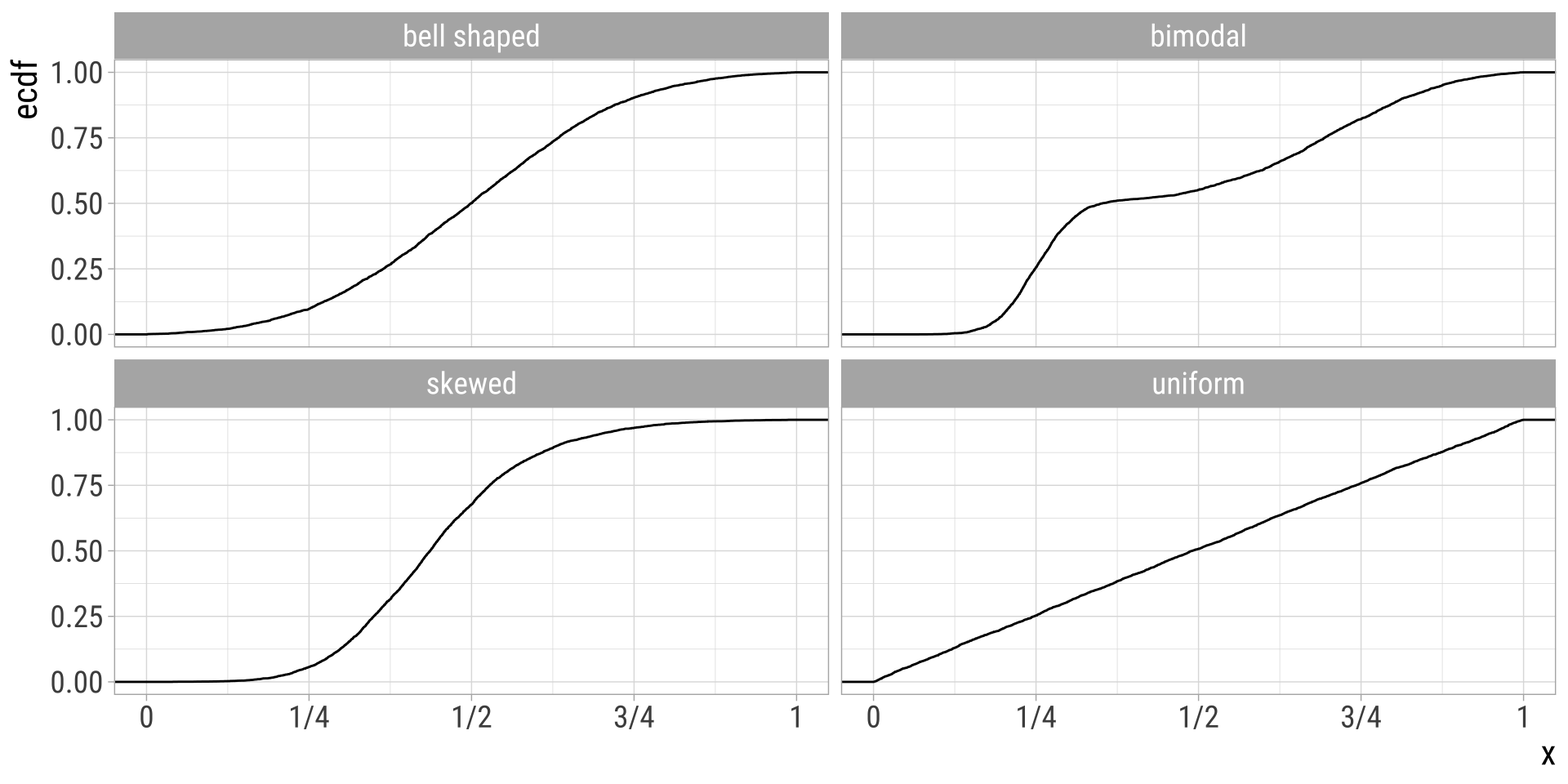
Less common plots for one numerical variable
These are more often used to look at the association between a numerical and a categorical variable:
- Boxplots
- Violin plots
- Strip charts
Two or more variables …
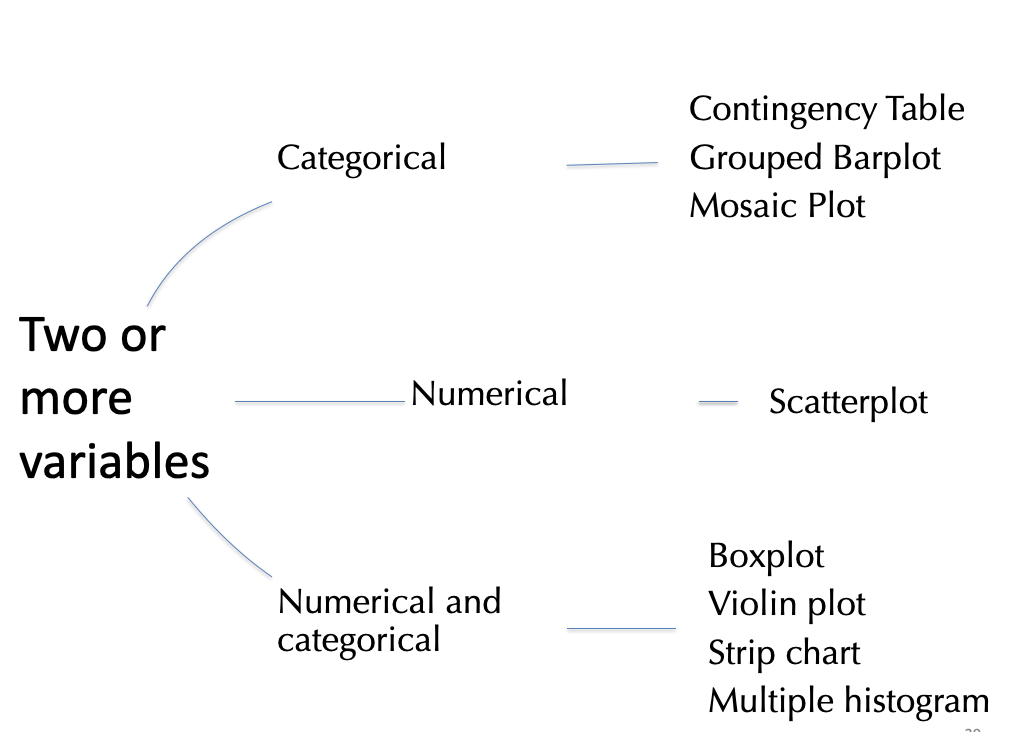
Categorical x Categorical
Contingency Table
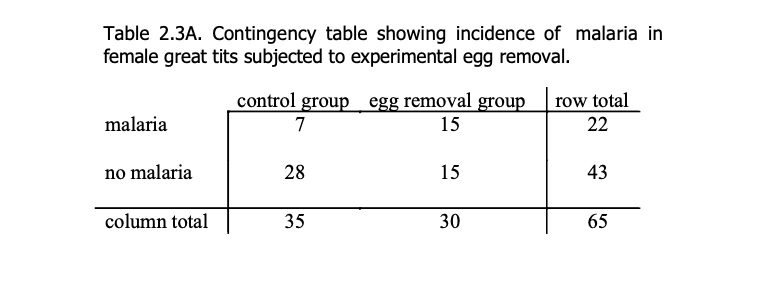
From: Whitlock & Schluter, The Analysis of Biological Data
Categorical x Categorical
Grouped bar plot
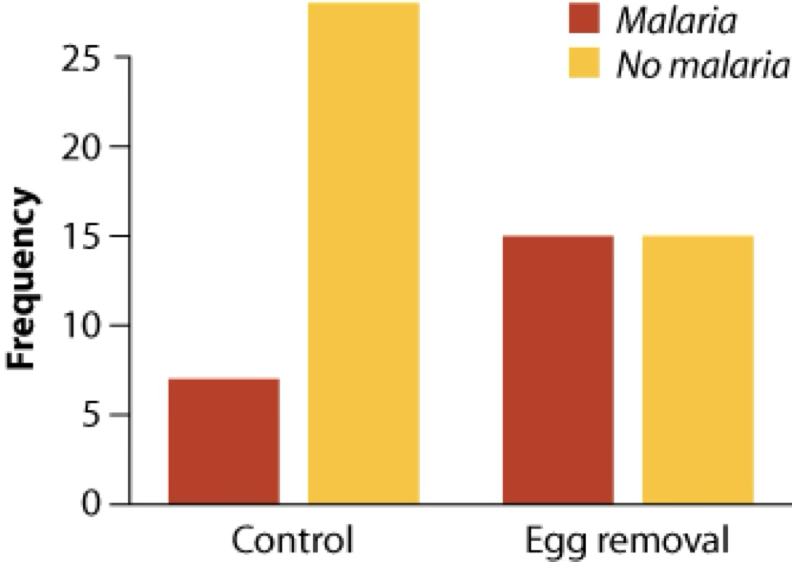
Figure caption: figure 2.3-1 from Whitlock & Schluter, The Analysis of Biological Data
Categorical x Categorical
Mosaic plot
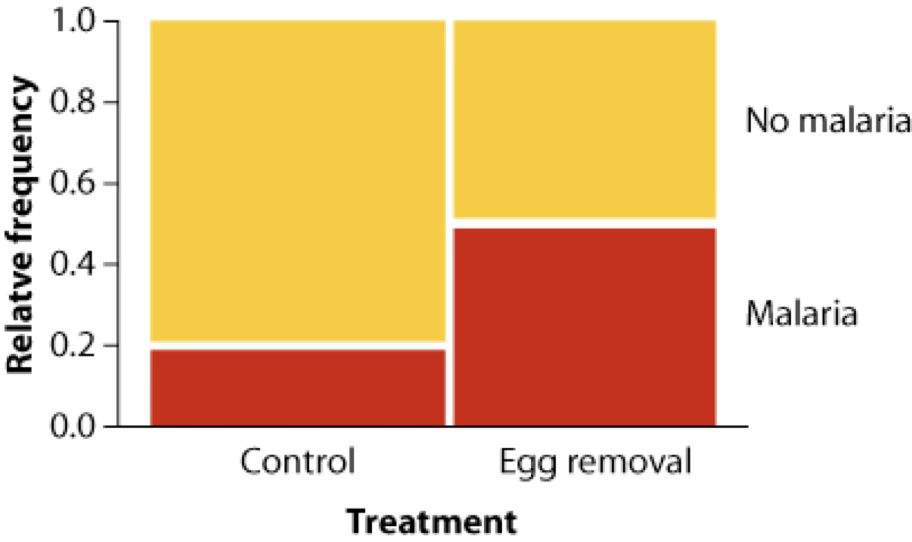
Figure caption: figure 2.3-2 from Whitlock & Schluter, The Analysis of Biological Data
2+ variables. No upper limit, but too many variables may be confusing
Width indicates the relative proportion of the corresponding value
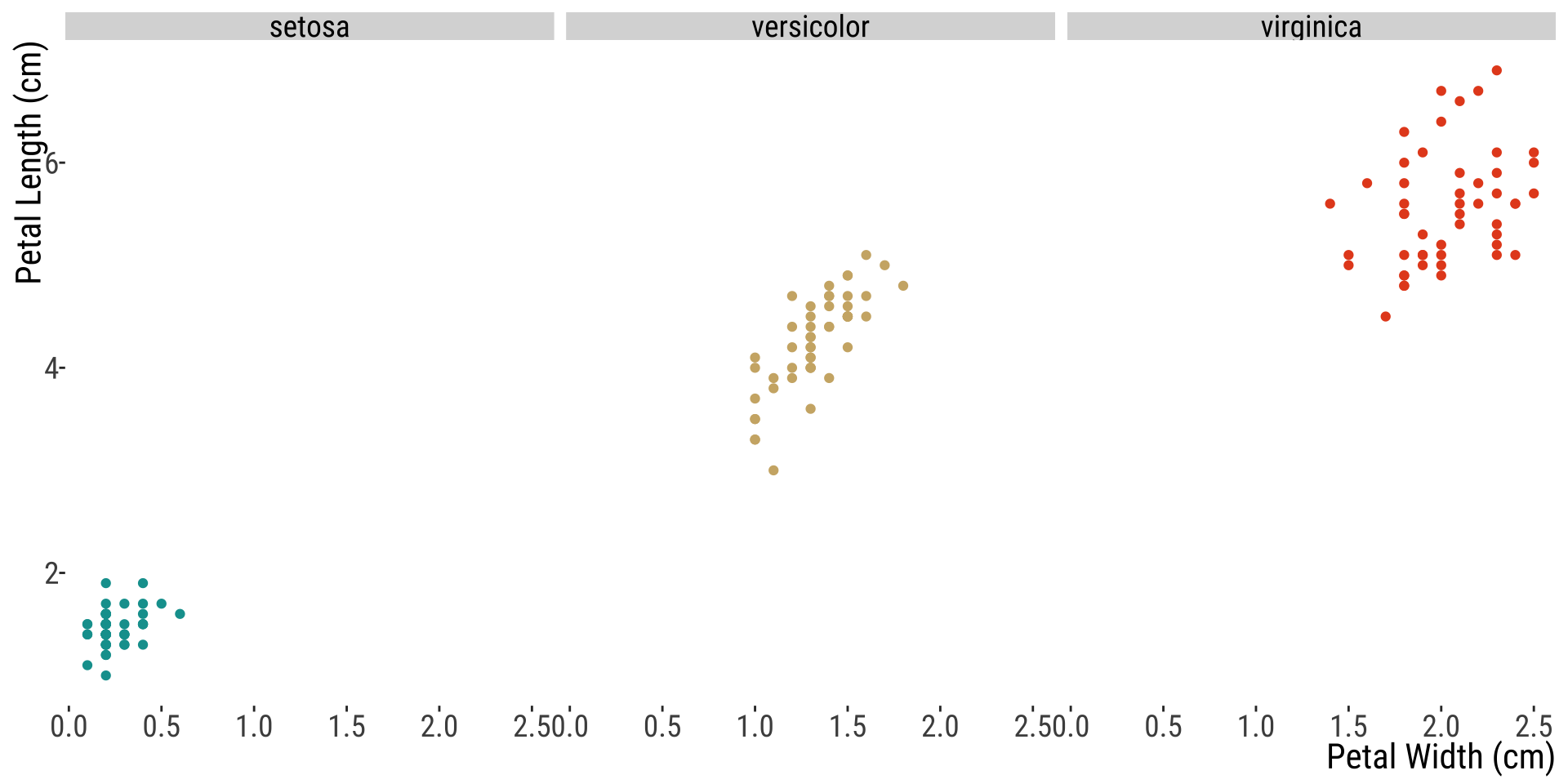
Numerical x Numerical
Scatter Plot
Numerical x Numerical
Scatter Plot
Numerical x Categorical
Multiple Histograms
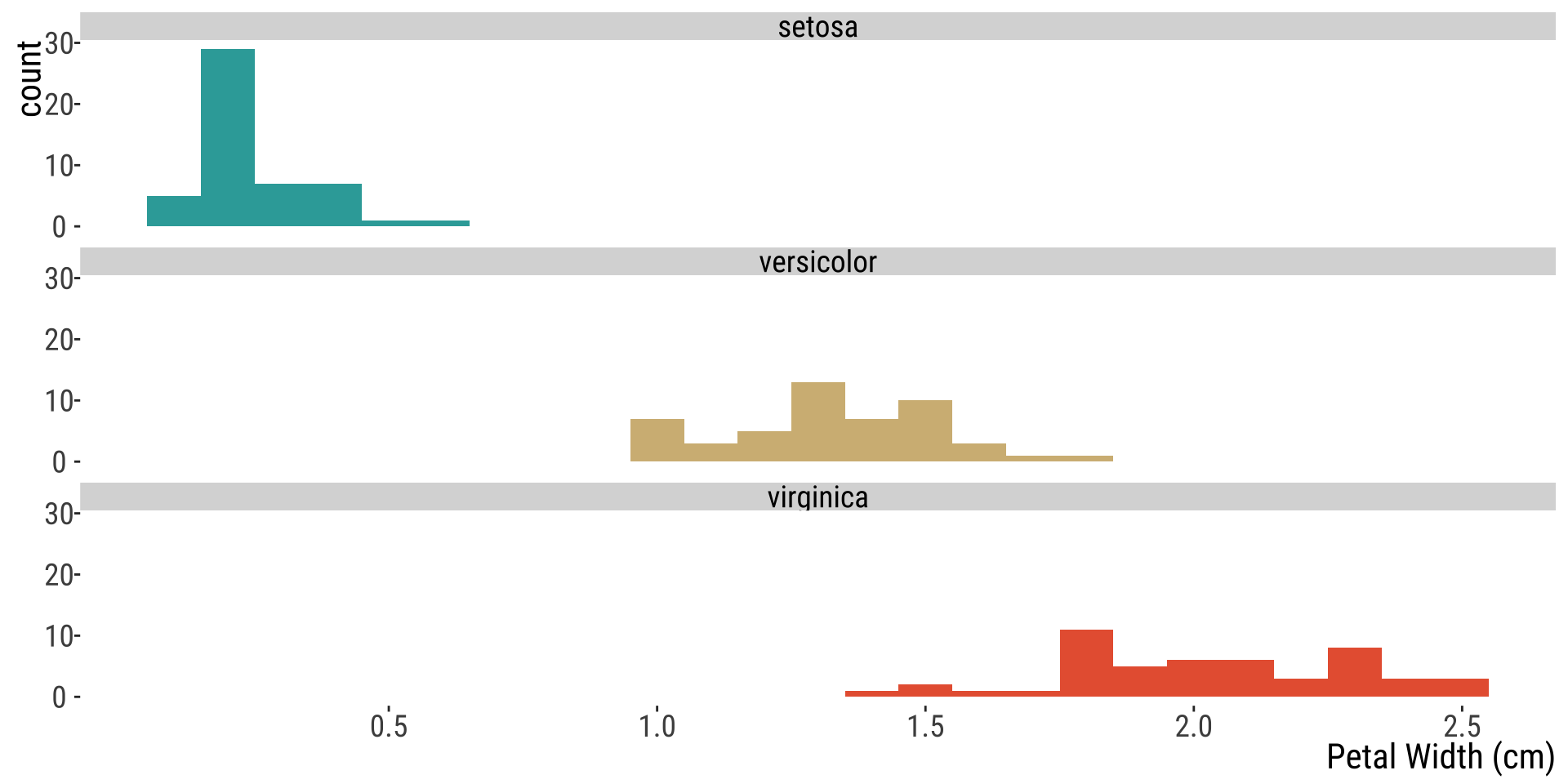
Numerical x Categorical
Strip Chart
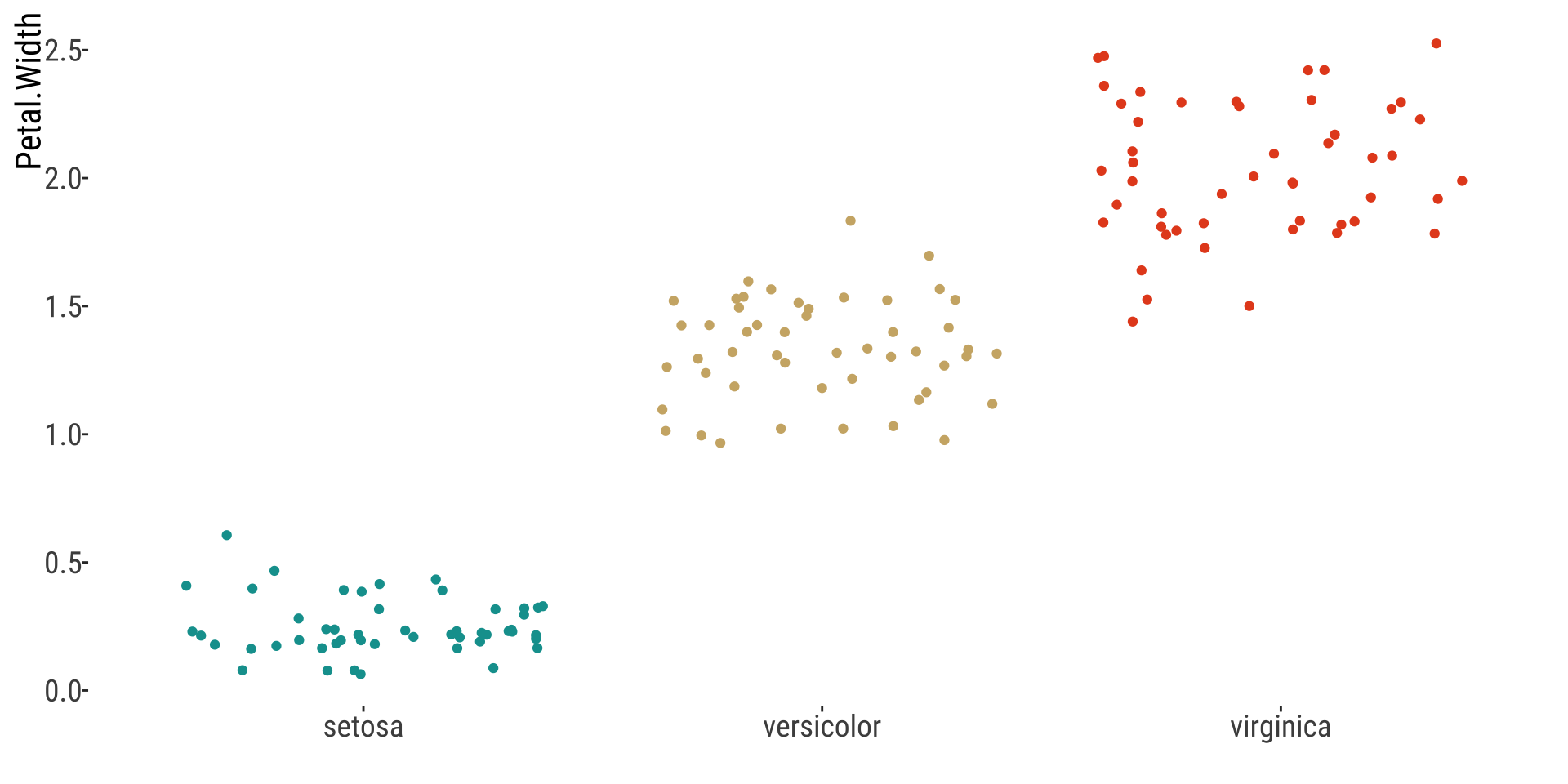
Numerical x Categorical
Boxplot
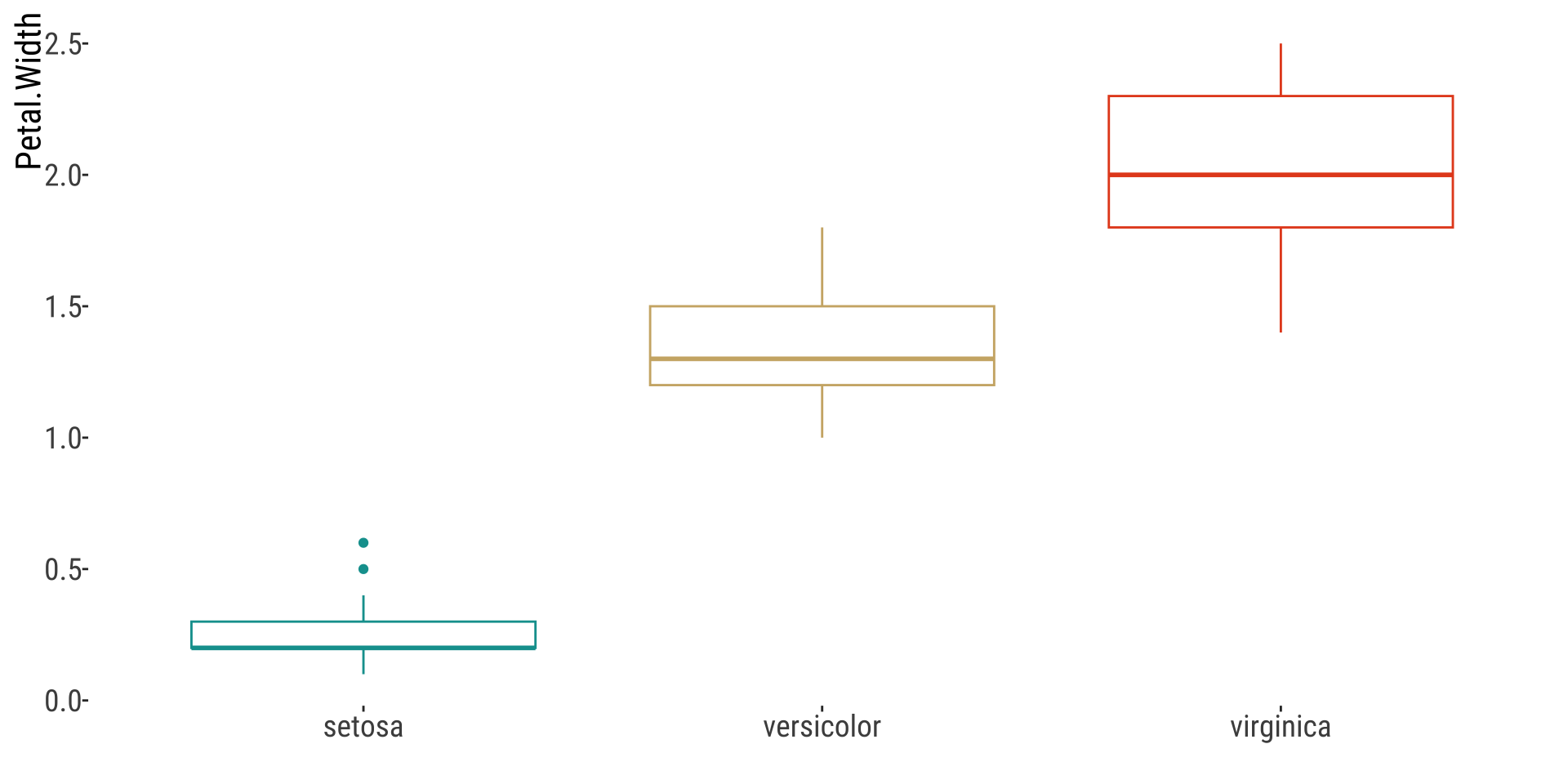
Numerical x Categorical
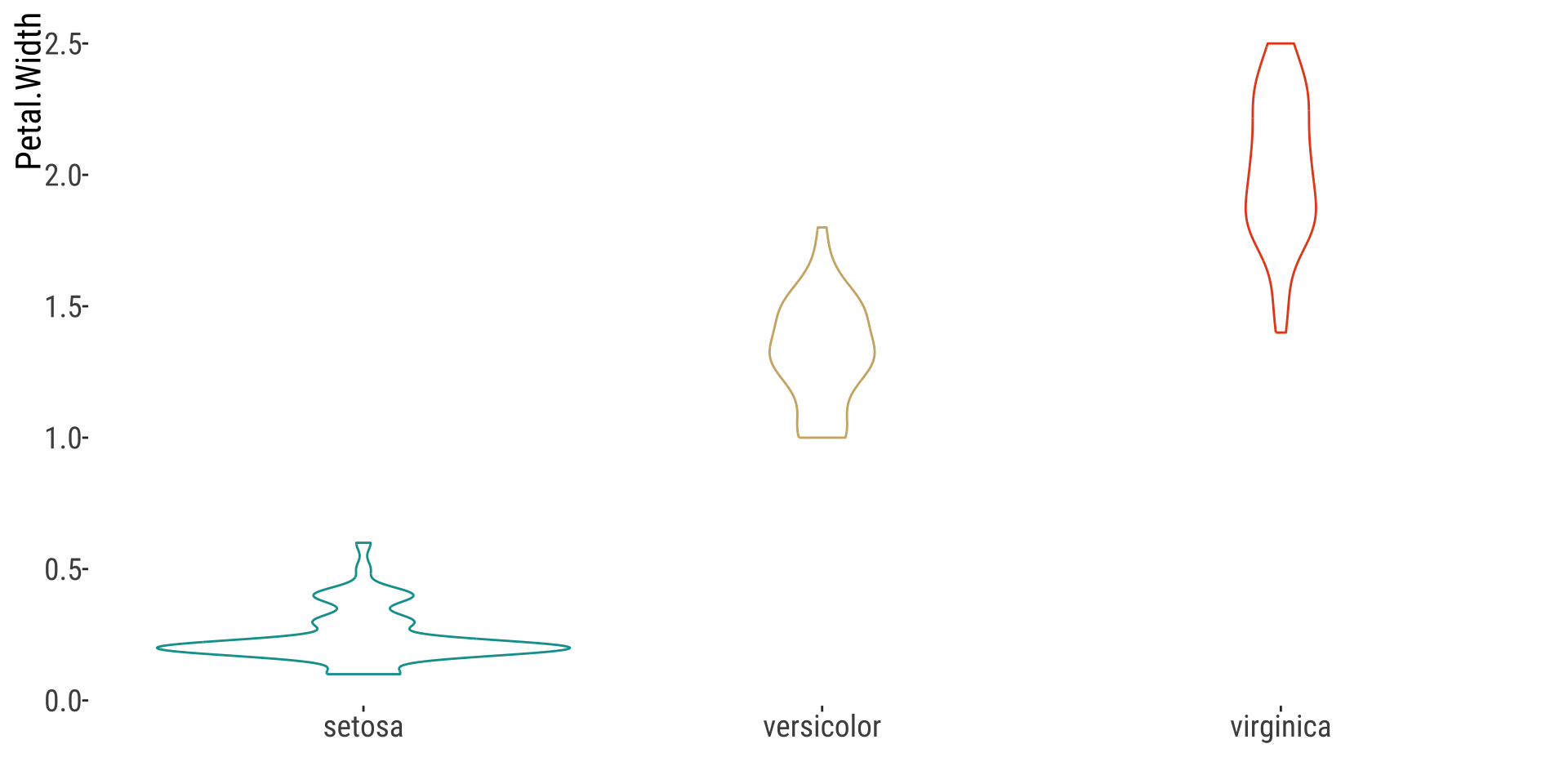
Violin Plot
Numerical (2) + Categorical
Multiple Scatterplots with legend
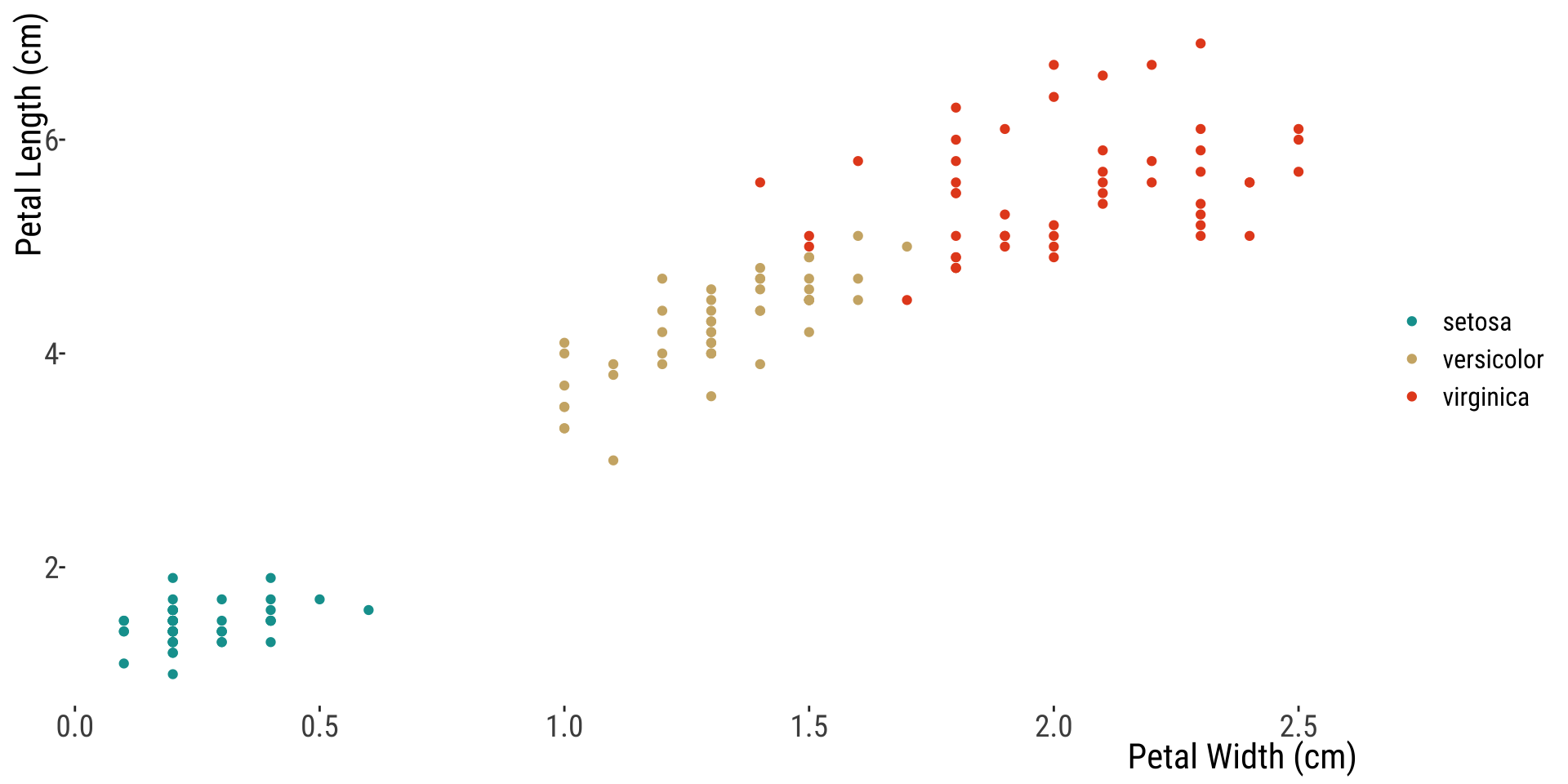
Numerical (2) x Categorical
Multiple scatterplots plotted separately
Visualizations Over Time and Space
Line Graphs Show Data Over Time
For temporal data, note all observations with a data point, and connect each point with a line.
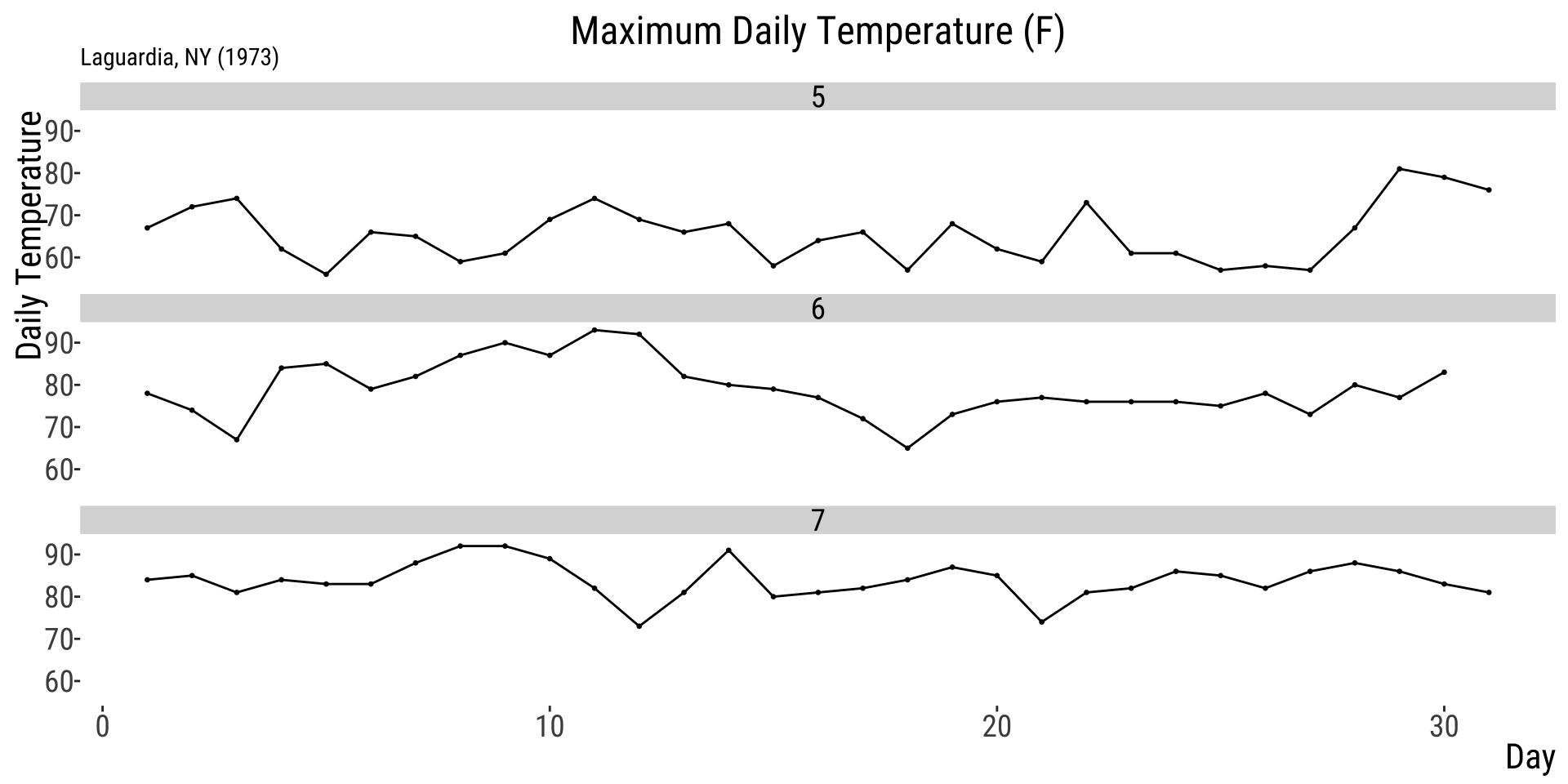
Small multiples line chart
A grid of line charts that uses the same scales and axes
To show spatial data
Maps
Spatial data does not have to be a geographical map
How to make good plots
- Show the data.
- Make patterns easy to see.
- Display magnitudes honestly.
- Draw graphics clearly.
Mistakes in displaying data:
- Hiding the data
What is the main problem here?
- Hide the data.
- Make patterns hard to see.
- Display magnitudes dishonestly.
- Draw graphics unclearly.
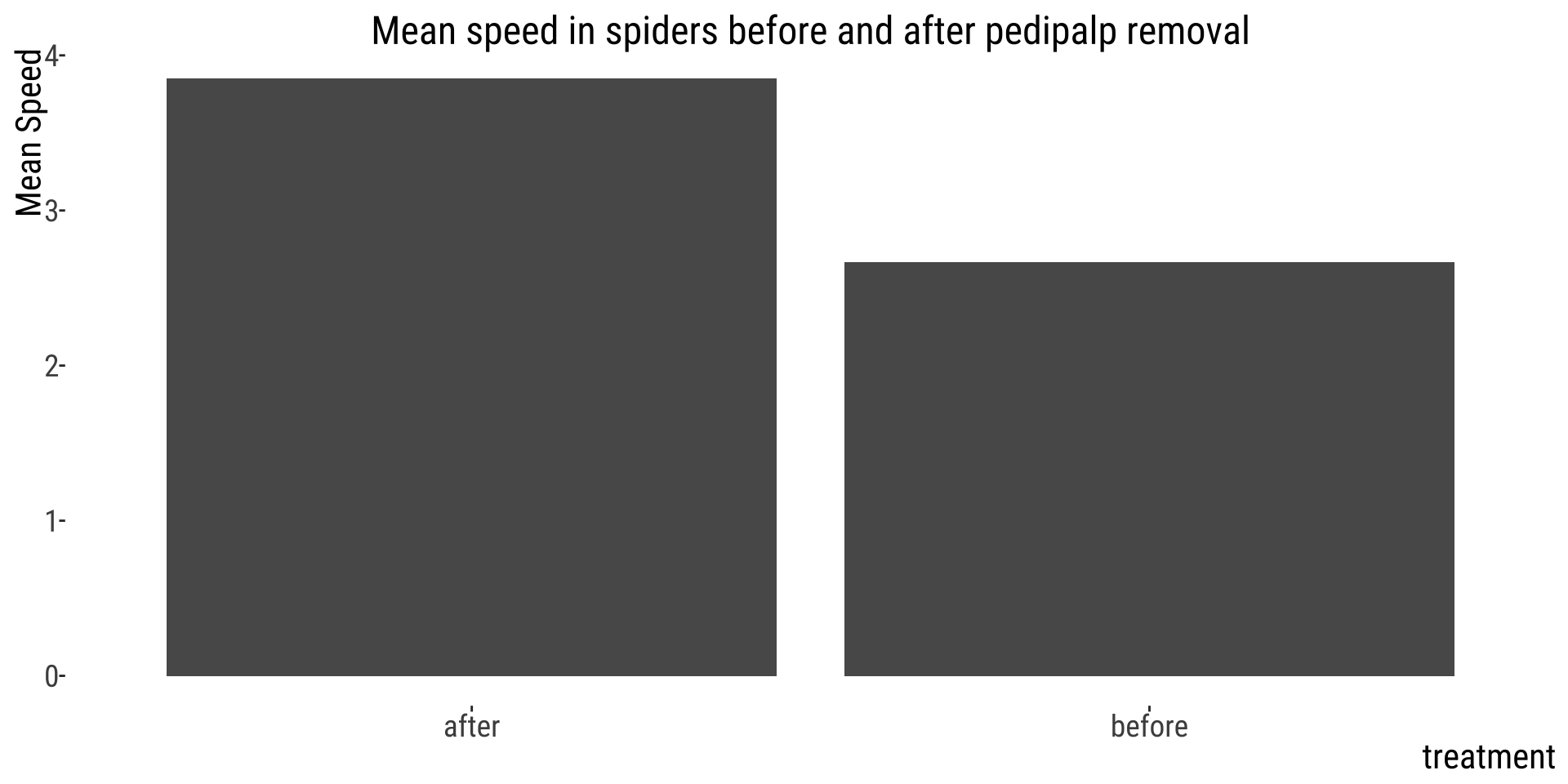
👎 Not showing data, just summaries
- Hide the data.
- Make patterns hard to see.
- Display magnitudes dishonestly.
- Draw graphics unclearly.
This plot hides the variation between positions.
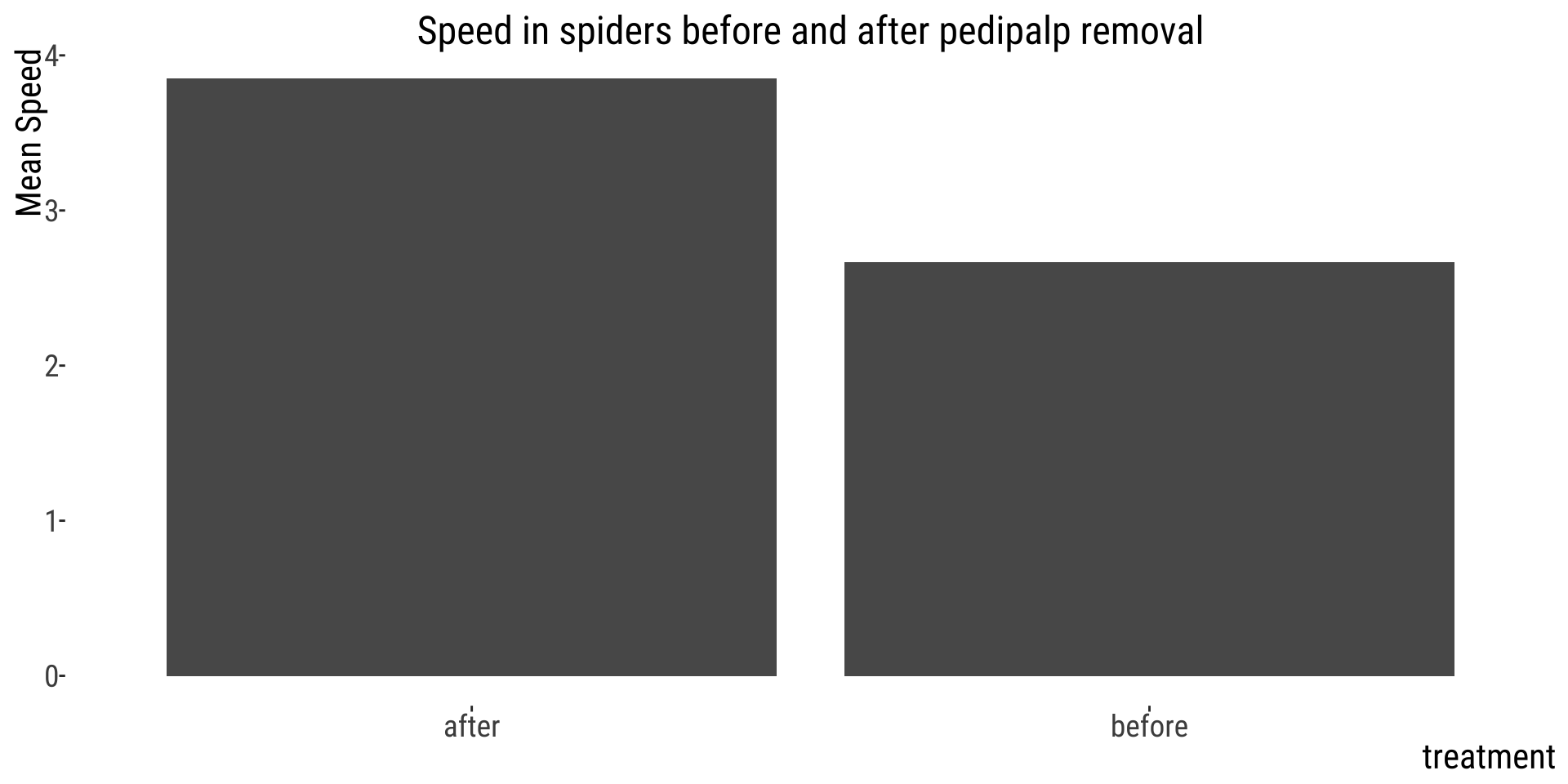
What is the main problem here?
- Hide the data.
- Make patterns hard to see.
- Display magnitudes dishonestly.
- Draw graphics unclearly.
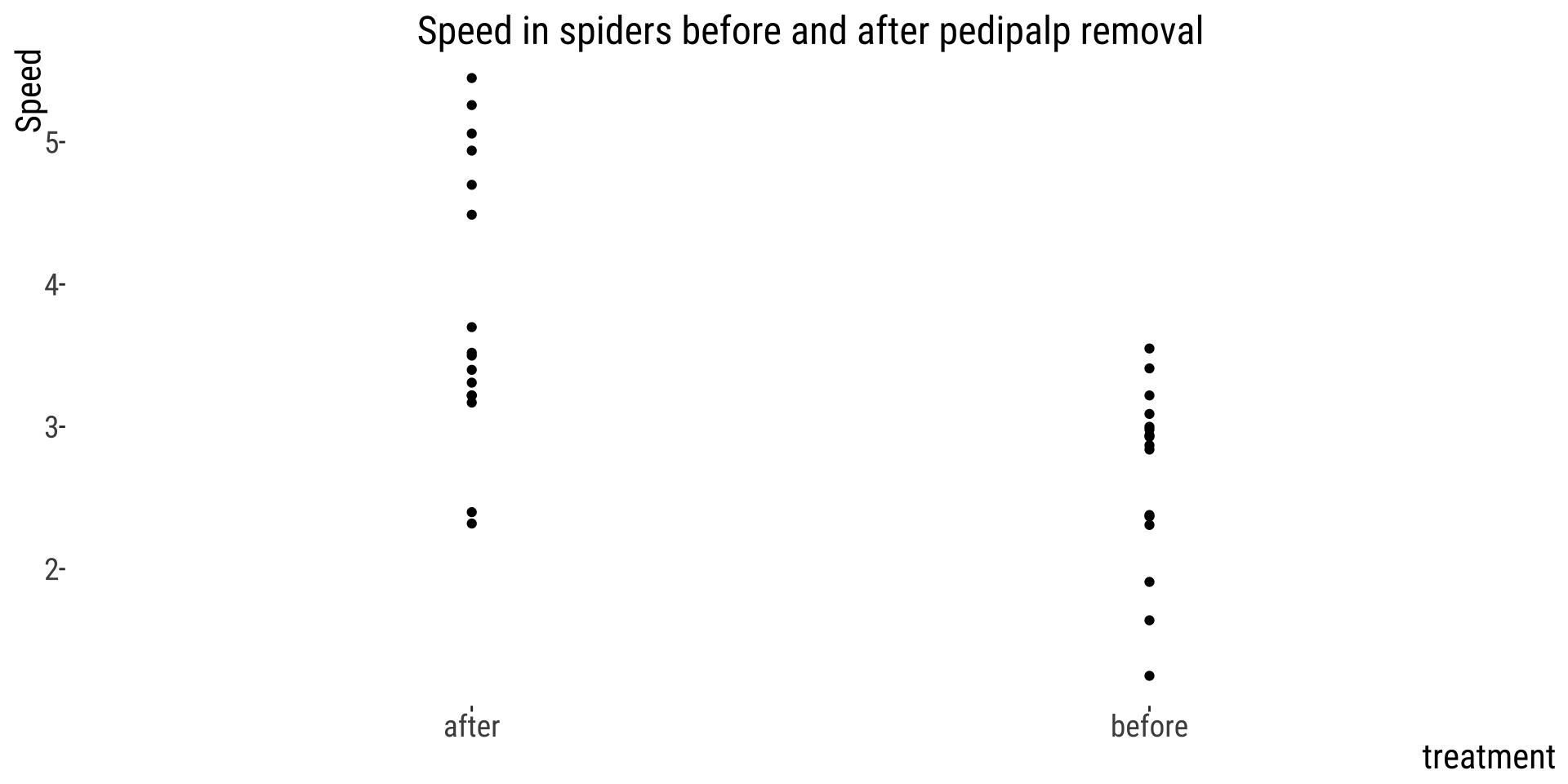

👎 Not showing data, overplotting
- Hide the data.
- Make patterns hard to see.
- Display magnitudes dishonestly.
- Draw graphics unclearly.
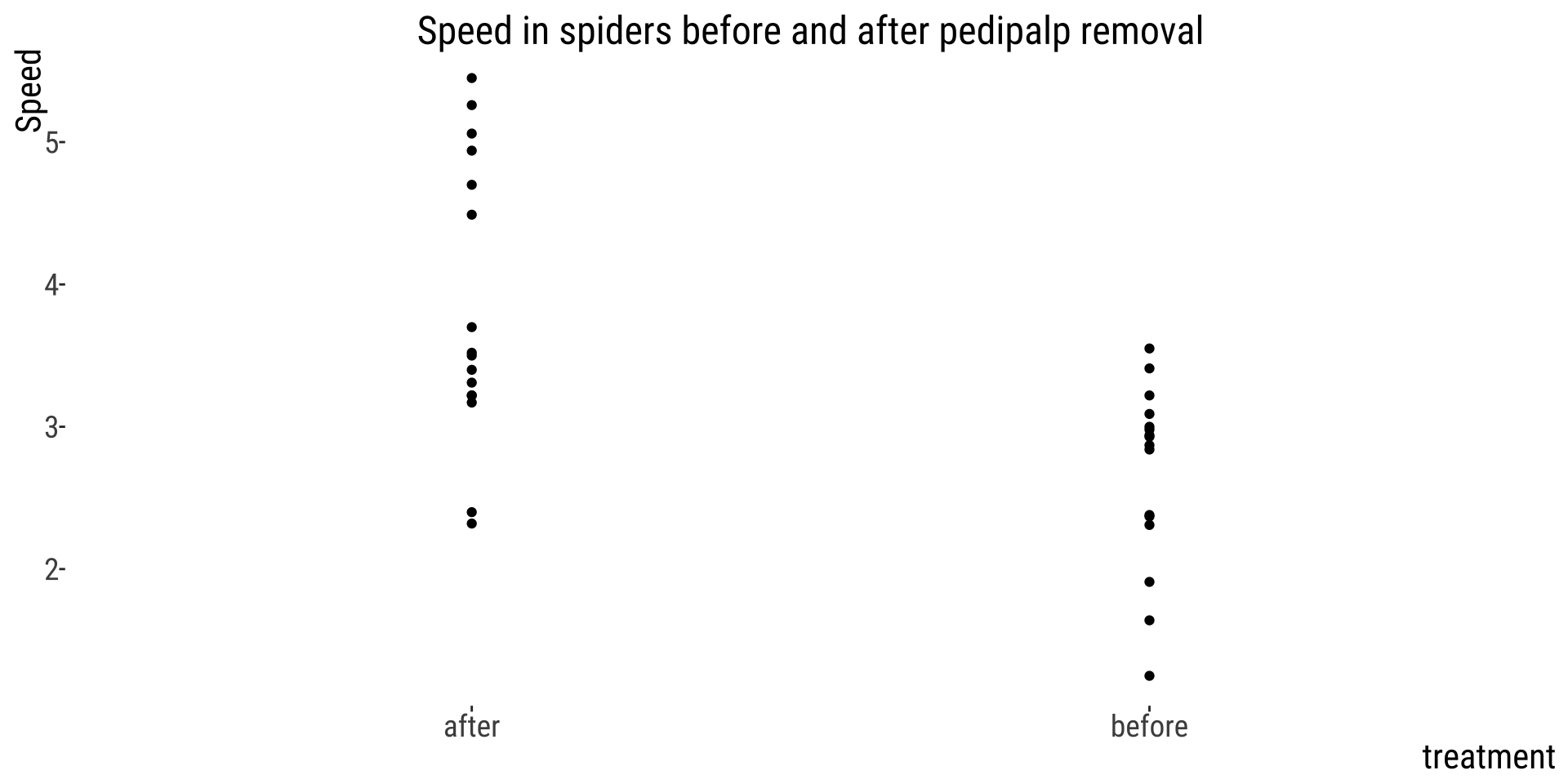

Over-plotting hides data by placing data points on top of each other.
👍 Showing data by jittering
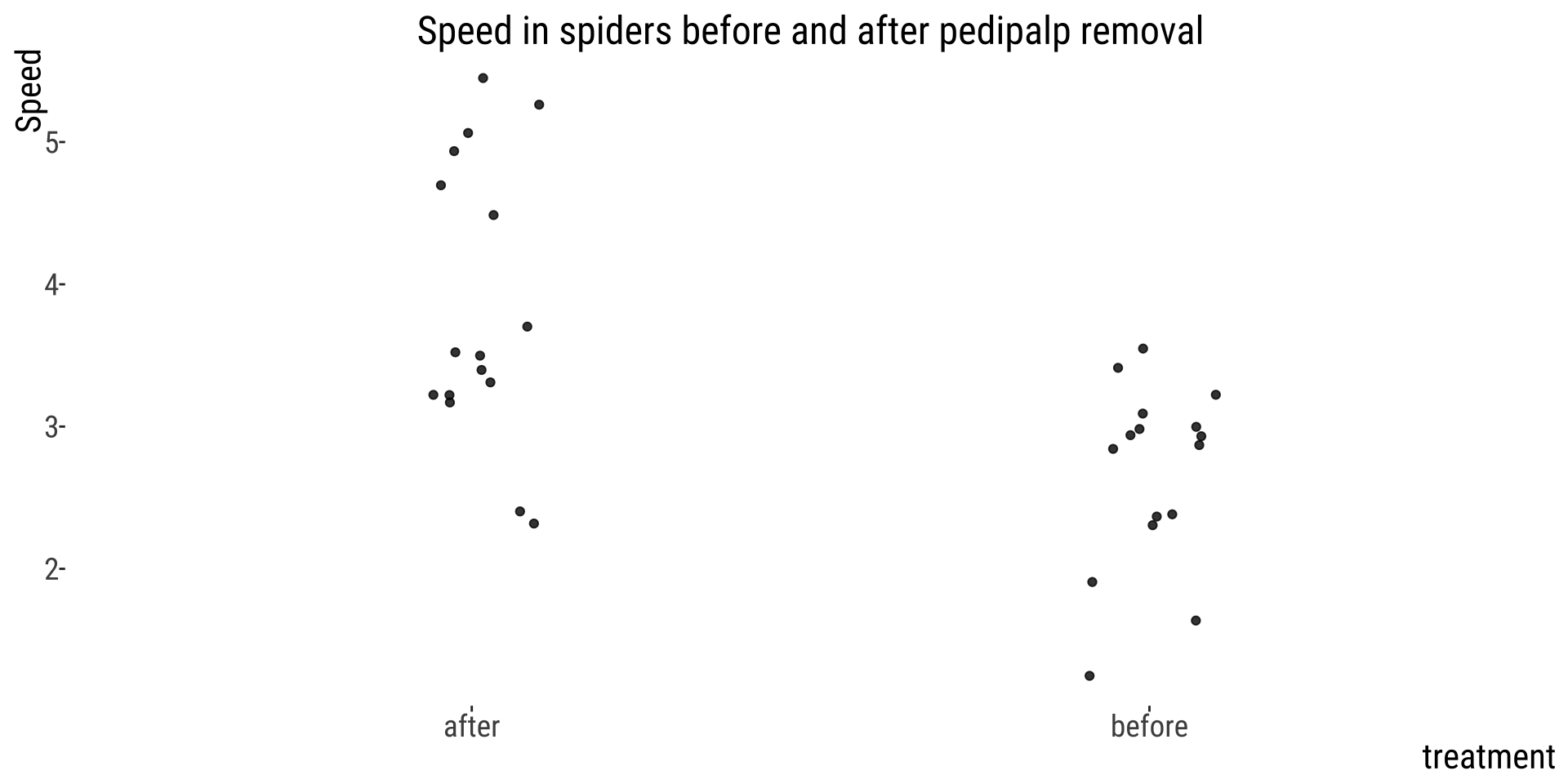

This plot shows all the observations
👎 How to hide data
- Provide only statistical summaries.
- Over-plotting - too many points.
👍 How to reveal data
- Present all of the data points.
- Allow all points to be seen.
Mistakes in displaying data:
- Making patterns hard to see
What’s the main problem here?
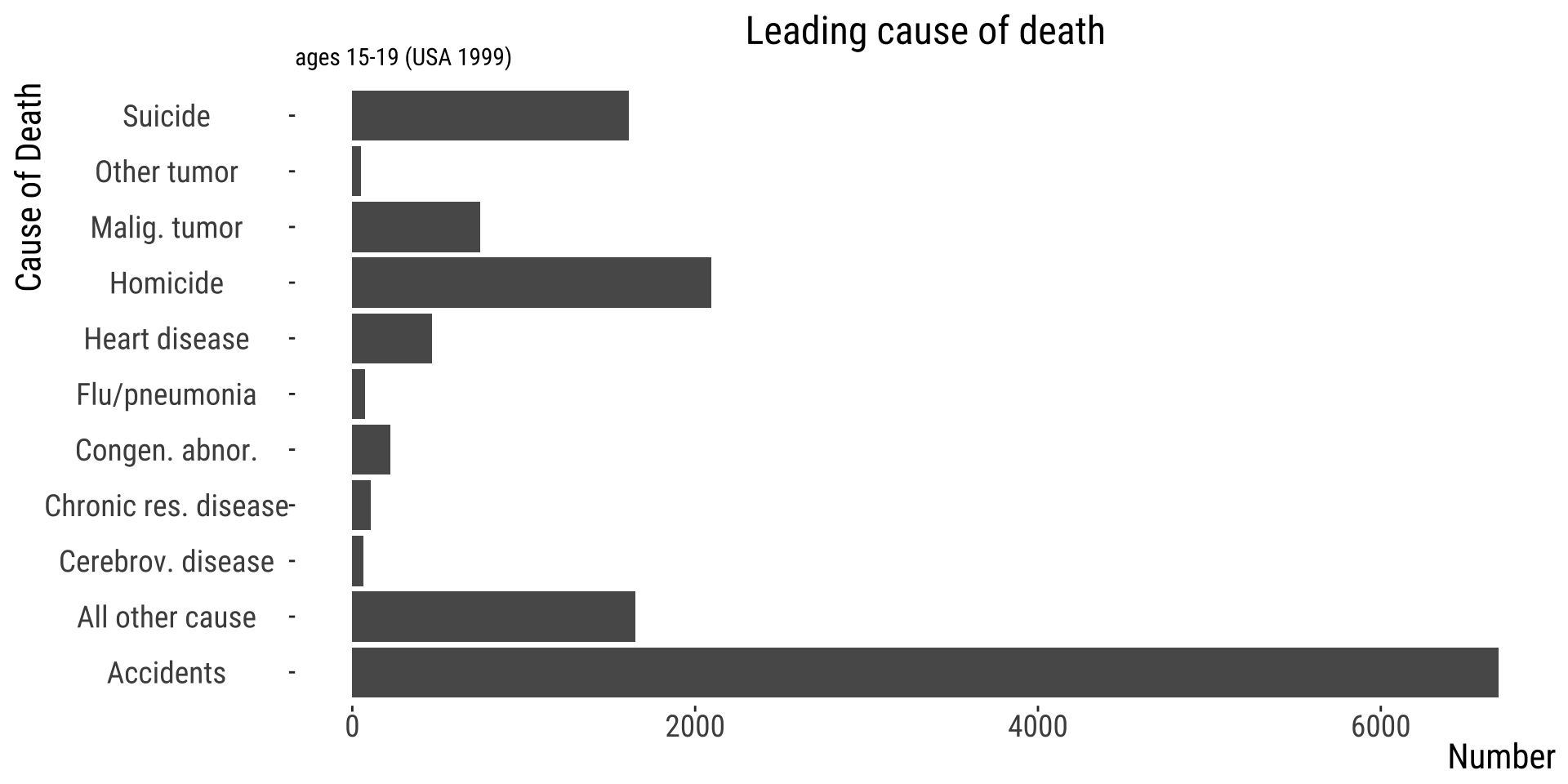
Nonsensical order hides pattern
Reordering factors makes pattern clear
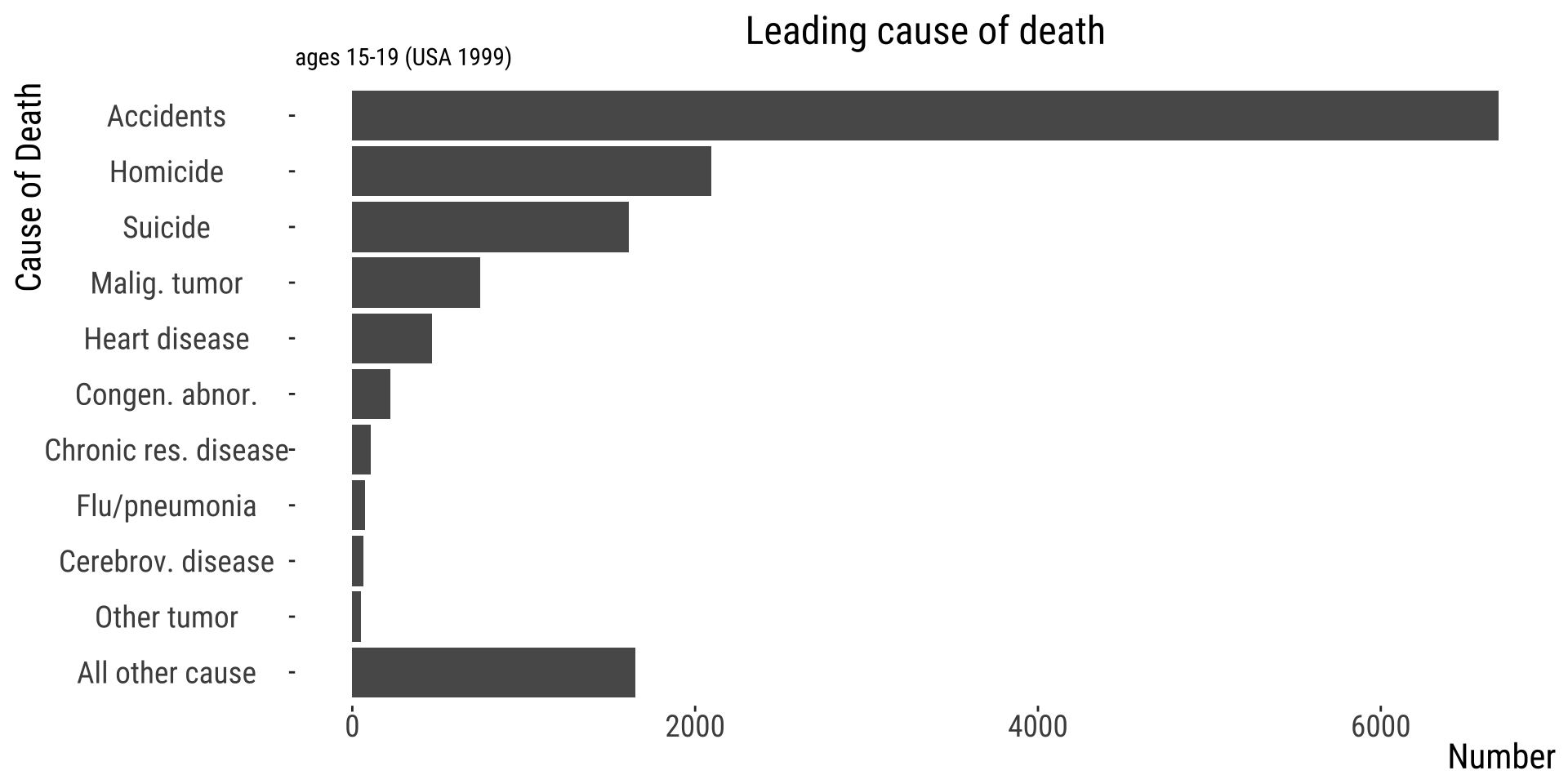
Tables should follow similar rules
| Cause_of_death | Number |
|---|---|
| Congen. abnor. | 222 |
| Heart disease | 463 |
| Accidents | 6688 |
| All other cause | 1653 |
| Other tumor | 52 |
| Suicide | 1615 |
| Homicide | 2093 |
| Chronic res. disease | 107 |
| Cerebrov. disease | 67 |
| Flu/pneumonia | 73 |
| Malig. tumor | 745 |
👎
Nonsense order hides patterns
Alphabetical order is usually a bad idea.
Tables should follow similar rules
| Cause_of_death | Number |
|---|---|
| Accidents | 6688 |
| Homicide | 2093 |
| Suicide | 1615 |
| Malig. tumor | 745 |
| Heart disease | 463 |
| Congen. abnor. | 222 |
| Chronic res. disease | 107 |
| Flu/pneumonia | 73 |
| Cerebrov. disease | 67 |
| Other tumor | 52 |
| All other cause | 1653 |
👍
Order to reveal patterns
List ordinal factors in a meaningful order
List nominal factors from greatest to least, with “all others” last.
How to hide patterns 👎
- Make one plot and call it good
- Unreasonable scales
- Arrange factors nonsensically
How to reveal patterns 👍
- Explore multiple potential plots
- Use appropriate scales
- Arrange factors meaningfully
- Order ordinal factors meaningfully (e.g., January to December.
- Order nominal factors by count
- If there is a grab bag category, place it after the lowest count
Problem?
Bad Axis-Limits Hide Patterns 👎
In this plot, the large scale hides the pattern (difference between the two groups)
That’s all for today

From: makeameme.org
B21: Biostatistics with R